Top 5 reasons to start experimenting with autonomous delivery robots now
The question is no longer whether robots will have their place in the supply chain, but when and how exactly they will be integrated into it – and which businesses will be the first ones to use this to their advantage.
Autonomous technologies are progressively maturing and can offer numerous benefits, such as cost efficiency, reliability, and improved performance, among others. That’s also why we believe now is the perfect time to start experimenting with autonomous delivery robots and look for ways to implement them in your supply chain.

Our robot at one of its latest demonstrations at the Innovation Days of Les Mousquetaires, one of France’s largest retail groups
Organizations who think strategically about automation and want to increase both business value and operational efficiency are already experimenting with robots and are looking to seize opportunities for early adoption. In their ranks, you’ll find Nokia, EDF, and DB Schenker, who are currently working with LMAD to integrate robots into their operations – among many other companies that are actively looking to test autonomous robots.
We could also draw a parallel between autonomous mobile robots (AMR) in warehouses and autonomous delivery robots (ADR): In warehouses, AMRs are in high demand at the moment, as they enable companies to automate operations and stay competitive. The same will happen outside of warehouses with delivery robots in the next few years.
In this article, we’re discussing the most important reasons why you should join them and consider conducting your first experiments with autonomous delivery technologies.
The current state of affairs – and why it’s important to start thinking about autonomous delivery now
The level of maturity of both the technology and the surrounding business environment and legislation are major factors – and in this regard, Europe is lagging behind North America and East Asia.
Currently, large-scale deployments are still a challenge in the EU and the rest of the continent due to the complex patchwork of national, regional, and local regulations, which are difficult to navigate for logistics companies.
But this doesn’t mean you shouldn’t start thinking about implementing autonomous delivery robots (ADRs) in your supply chain – on the contrary, that’s exactly why it’s crucial for European businesses to act now and be prepared. As soon as the right business and legislative environment becomes a reality, the progression will be rapid. The technology is already burgeoning in different parts of the world and we’re at a crucial stage where breakthroughs will lead to major shifts in the business.
Major legislative advances are also happening right now: in Germany, as of 2022, the German Federal Council is in the process of regulating the conditions in which autonomous vehicles can operate in predefined areas, which is seen as a major breakthrough. In December 2019, France adopted a new mobility orientation law to allow the use of autonomous vehicles as early as 2022, under specific conditions.
Such legislative developments are a major milestone in the development of autonomous delivery in Europe. In 2024-2025, both the legislation and the technology’s maturity will allow for real-life deployments of autonomous delivery robots for selected use cases.
Deloitte’s current recommendation for businesses is to actively monitor developments and invest in automation technologies to be able to quickly implement autonomous robots at different stages of their supply chains.
Package and food delivery are both huge markets that are rapidly growing; currently they’re estimated at $170+ billion and $151 billion globally, respectively, with food deliveries having more than tripled since 2017. Profitability, however, is under question for many businesses, and margins remain low, as pointed out in a report by McKinsey & Company.
To tilt the scales in the right direction, companies need to find ways to optimize their delivery operations in a quick and efficient manner – and autonomous delivery robots can help, along with the optimization of delivery routes (with the help of the right AI technology) or the consolidation of multiple orders in a single delivery round (which AI can also help with).
This means that conducting pilot experiments should be a priority for businesses that wish to seize the potential of autonomous technologies early on – and improve operational efficiency.
LMAD and other companies are already experimenting with open-road autonomous deliveries. Due to more flexible upcoming regulations and the growing demand for cheaper and greener urban logistics, now is the time to begin experimenting in public areas. Additionally, private sites and gated areas (such as private facilities, campuses, and industrial sites) allow for faster deployments and implementation.
The long-term advantages of using autonomous delivery robots
Using autonomous delivery robots has many potential long-term benefits. Not all of them will or can be realized at the current moment; nevertheless, they’re important to consider when deciding on investment priorities.
Let’s look at the most important ones.
Robots can:
1. Improve the speed and accuracy of routine operations
Routine operations are the first to benefit from automation, especially in warehouses and at manufacturing sites, where autonomous robots are already firmly present.
Last-mile delivery, which is typically the most challenging part of the supply chain, can also be vastly improved with the help of ADRs, which can be quick and efficient in carrying and dropping off parcels at pre-selected delivery points. Loading and unloading the robot can also be optimized, as it can happen outside of busy city centers, at flexible times, and multiple deliveries can be combined based on the physical proximity of recipients.

Our robot during one of our experiments in Helsinki in 2021
In use cases where the same delivery route needs to be followed consistently every day, with the same stops, autonomous robots are ideal, because they can guarantee a high degree of reliability and service locations in a highly optimized manner. For example, such a use case could be the restocking of inventory for multiple retail stores, supermarkets, and restaurants on a busy shopping street, or other instances of routine B2B delivery operations.
2. Improve overall efficiency and safety when working alongside humans
Low-value, mundane, repetitive, or high-risk tasks are prime candidates for automation with the help of autonomous robots.
If you’re looking to optimize efficiency, having humans work on tasks with a higher added value (rather than on simple, routine tasks) makes sense. This way, you’re also increasing employee productivity and making better use of human potential and ingenuity in your operations.
Contrary to what you might expect, integrating autonomous robots in your supply chain in a sensible manner can also improve employee motivation, since workers will no longer be busy with low-value, high-risk tasks but can tackle more strategic and complex challenges – and see the results of their work.
Robots can work consistently on high-risk tasks that humans “cannot, should not, or do not want to do” with a high degree of accuracy and precision. This helps improve workers’ personal safety – and delivery work is not exempt from risk. Drivers and bike couriers have road accidents and can suffer from various injuries: In the UK, a significant portion of workplace vehicle accidents happen during deliveries (and the same is likely true elsewhere).
According to a study conducted by University College London (UCL), 42% of drivers or couriers working in the gig economy had already had road accidents – and 10% of all respondents report someone has suffered an injury as a result (most frequently, themselves).
For this reason, safety considerations are crucial, not only in manufacturing, but also in delivery operations. In addition to that, contrary to human drivers, who are often tempted to not respect all rules, robots strictly adhere to traffic regulations, further contributing to everyone’s road safety.
3. Help solve labor shortages and ramp up capacity as needed
Robots can also help address labor shortages, and typically these occur exactly for occupations that are of relatively low overall value or highly repetitive. Robots can actually make humans’ work more meaningful by enabling them to shift to tasks with a higher added value.
Labor shortages are particularly prominent with seasonal increases in demand – for example, during the winter holiday season, delivery demand sharply increases, which can result in delays and considerably decrease customer satisfaction. During periods of high demand, parcels often end up rerouted to random pick up points, which can be many kilometers away.
With autonomous robots, you’ll be able to easily ramp up your delivery capacity, even during exceptionally busy periods. Robots, especially with the help of AI and ML technology, are scalable and flexible, improving efficiency even on a short notice.
Minus the time needed for charging or swapping their batteries, robots can operate 24/7 and thus increase delivery speed and performance.
They can deliver early in the morning or late at night, which can be particularly valuable for industrial sites or when replenishing inventories for retail stores.
4. Help provide an excellent customer experience
Customers demand convenience and speed – and since the Covid-19 pandemic these demands have only increased. With robots, you can provide both, since they’re at the core of robots’ capabilities.
Robots can help increase logistics providers’ revenue by improving successful fulfillment rates, speed of delivery, and also customer satisfaction. They can deliver to different locations (including at customers’ doorsteps), serve as temporary pick-up points, and communicate with recipients automatically, enabling them to change the pick-up time or location, if needed.
In our experiment in Helsinki, for example, we were able to provide a mobile locker to customers at different locations that were underserved by other delivery methods, such as parcel lockers or pickup points. The survey we did after the experiment confirmed that residents expect convenience and hope that autonomous delivery robots will bring them that.
Contactless deliveries are another point of interest for many customers, and ADRs are perfect for this use case, as well. Robots have already been used in a hospital setting for non-contact deliveries of meals and medicine to patients, which can help curb the spread of infectious diseases; these benefits aren’t limited to specific uses in healthcare, though.
5. Reduce operational costs and the carbon footprint of the last mile
The last mile of delivery is the most expensive leg of the journey from supplier to customer, accounting in many cases for up to 53% of the total costs. According to Statista, last-mile delivery in 2018 cost over $10, while customers were charged $8, but were actually willing to pay only $1.40 for it:
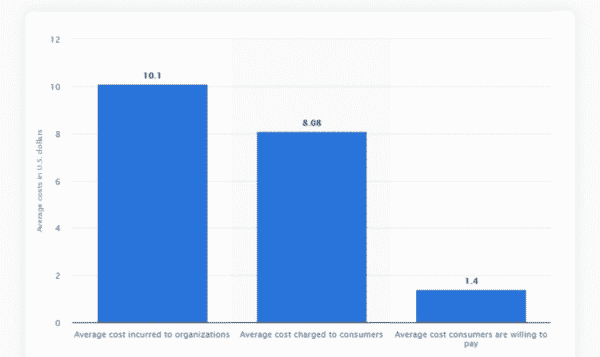
There’s a large gap between customers’ willingness to pay for delivery and the actual cost incurred (source: Statista)
Amazon can absorb delivery costs and provide free delivery, which customers are now accustomed to, but smaller operators often cannot – meaning that there’s a clear problem with the financial sustainability of delivery operations.
It’s clear that with small-scale deployments, robots remain an expensive alternative that also requires navigating complex legal requirements. As with any technology, before widespread adoption, costs are high and the return on investment isn’t always immediate – or as high as expected.
As large-scale deployments start becoming reality, however, robots can become more and more cost-efficient and help operators provide convenience and speed at a competitive price – while also significantly reducing the carbon footprint of the last mile.
This means that robots can help companies gain a competitive edge and solve the riddle of the last mile of delivery, which is disproportionately expensive because of its complexity and associated labor costs, and disproportionately polluting, too.
In large-scale deployments, delivery robots could help reduce costs in the following ways:
- Improve efficiency, performance, and reliability
- Reduce labor costs
- Eliminate fuel expenses, which are substituted with electricity costs
- Optimize delivery routes and parcel distribution
- Reduce liability expenses for employees’ work-related accidents by improving safety
- Reduce customer complaints about deliveries
As they’re electric and generally much lighter, robots have a significant advantage over delivery vans in terms of the ecological footprint of the last mile, which is also one of their key advantages.
We’ve discussed the topic in lots of detail in our article on the environmental impact of last-mile deliveries, but overall autonomous robots are continuously proving that they can be a viable alternative to deliveries by cars and vans, and produce less than 2% of the carbon emissions of vans.
To realize both the cost-associated and ecological benefits, it’s important to start thinking about experimenting with autonomous robots now, even before large-scale deployments are realistically possible: At the moment they become reality in Europe, progress will be fast and companies that already have the expertise and experience with autonomous delivery technologies will have a clear advantage to those that don’t.
Let’s now look at the short- and medium-term advantages of autonomous delivery
By making autonomous delivery experiments a priority, you’re ensuring that your organization will be future-ready and will have the capacity to implement robots at scale swiftly, when the timing is right. The best way to prepare your company for the future of deliveries is by analyzing opportunities and conducting experiments now, in order to gain sufficient exposure to the emerging technologies in the sector and prepare your workforce to use them in the future.
There are numerous advantages to this approach. This way, you can:
- Get familiar with the technology and its current capabilities to gather precious information and expertise
- Monitor the latest developments – and not just from afar – to know what’s on the horizon
- Be ready to implement quickly whenever the time is right
- Establish the right partnerships with robot suppliers, software vendors, and other suppliers and contractors
- Get familiar with the legislative framework in which you’ll operate and follow the latest developments
- Figure out the best way to automate each part of your supply chain and increase the business value of future implementations
- Boost your corporate brand image by investing in cutting-edge technologies and implementing a forward-thinking approach to your operations
Autonomous delivery technologies are progressively reaching a more mature stage, as is the legislative framework that would permit large-scale deployments and the business environment in which they can develop.
For this reason, businesses that understand their potential and are already looking for ways to implement them in their supply chains will have an important headstart when autonomous delivery robots become widely available: They’ll be better prepared to use their full capabilities and will have the technological and operational know-how and expertise to make the most of them.

